Generative AI is rapidly becoming part of everyday business workflows from writing content and analyzing data to generating code and supporting customer interactions.
But as adoption accelerates, so do the risks. Without a clear generative AI security policy, organizations expose themselves to data leaks, compliance violations, intellectual property loss, and reputational damage.
An effective generative AI security policy acts as a guardrail. It allows teams to innovate with AI while maintaining control, visibility, and accountability.
This article explains how to design, implement, and govern a generative AI security policy that balances innovation with security.
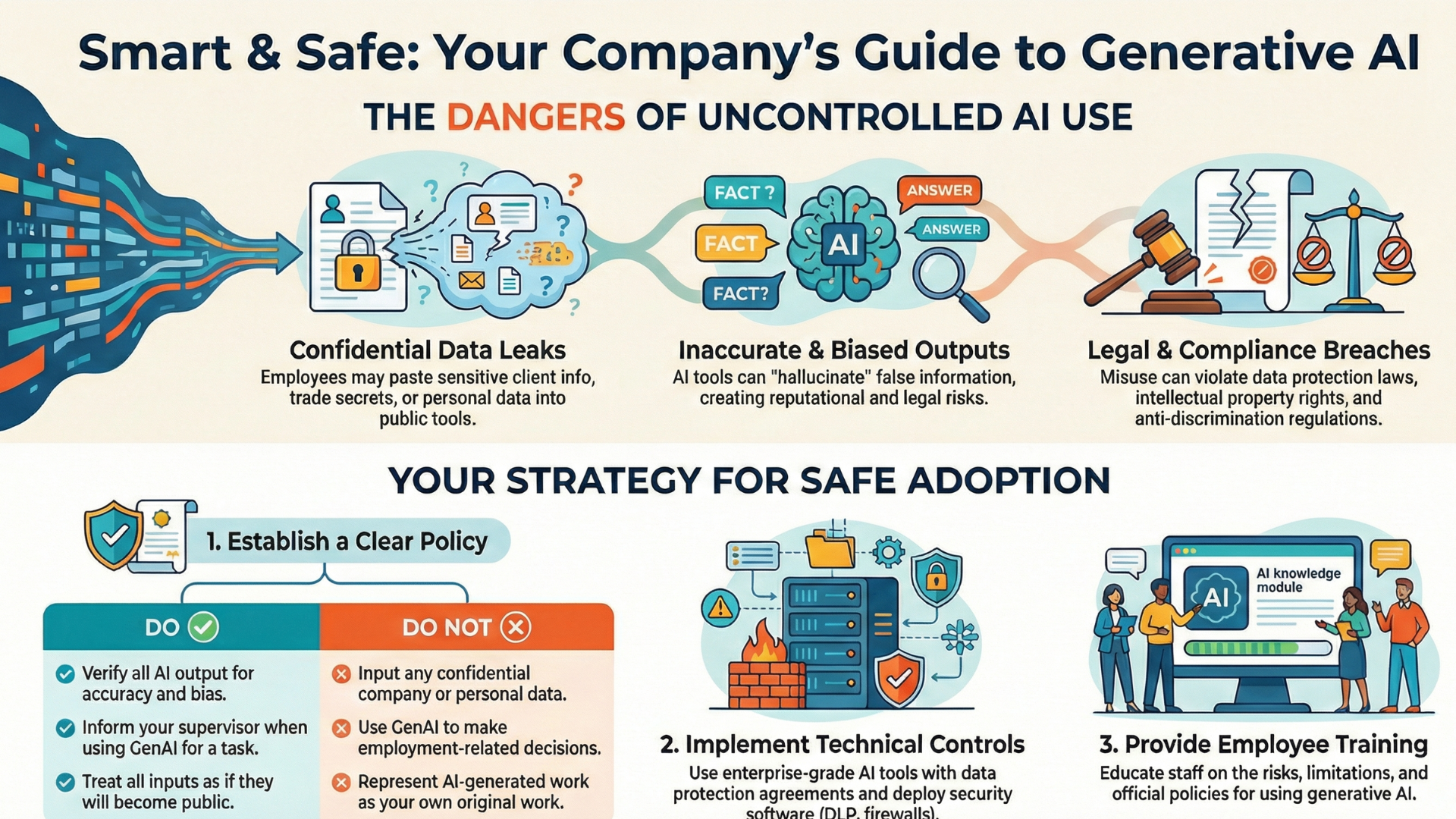
What Is Generative AI Security Policy
A Generative AI Security Policy is a formal set of guidelines that defines how an organization can safely use generative AI tools such as large language models, code generators, and image-generation systems without exposing data, systems, or intellectual property to risk.
The policy outlines who can use generative AI, for what purposes, and under what conditions. It typically addresses data protection rules (what data can or cannot be shared with AI tools), access controls, model usage boundaries, and compliance requirements. For example, it may prohibit employees from inputting sensitive customer data, source code, or confidential business information into public AI platforms.
A strong generative AI security policy also covers risk areas unique to AI, including prompt injection attacks, model hallucinations, biased outputs, and misuse of AI-generated content. It defines human-in-the-loop review processes, output validation standards, and accountability for AI-assisted decisions.
The policy sets requirements for vendor evaluation, logging, monitoring, and incident response related to AI usage. As generative AI adoption grows across teams, this policy ensures innovation happens responsibly balancing productivity gains with security, privacy, and regulatory compliance.
Why a Generative AI Security Policy Is No Longer Optional
Generative AI systems work by consuming large volumes of data and producing new outputs based on patterns. This creates unique security challenges that traditional IT policies were never designed to handle. Many employees already use public AI tools without approval, often sharing sensitive information unknowingly.
A generative AI security policy is essential because it defines what is acceptable, what is restricted, and how risks are mitigated. Without a formal policy, organizations face uncontrolled AI usage, inconsistent decision-making, and unclear accountability.
Key reasons a generative AI security policy is critical today include:
Employees entering confidential data into public AI tools
AI models retaining or reusing sensitive prompts
Unclear ownership of AI-generated intellectual property
Regulatory exposure under data protection laws
Lack of auditability for AI-assisted decisions
An effective generative AI security policy transforms AI from a shadow IT risk into a governed business capability.
Defining the Scope and Objectives of a Generative AI Security Policy
Every successful generative AI security policy starts with a clearly defined scope. Organizations must decide where generative AI is allowed, how it can be used, and which systems fall under policy enforcement.
Establish Clear Policy Objectives
The objectives of a generative AI security policy typically include:
Protecting sensitive and proprietary data
Ensuring regulatory and legal compliance
Reducing security and privacy risks
Enabling responsible AI innovation
Maintaining transparency and accountability
By clearly articulating these goals, organizations align security teams, legal teams, and business users around a shared understanding of AI risk.
Define What the Policy Covers
A comprehensive generative AI security policy should explicitly cover:
Public generative AI tools (e.g., chat-based AI platforms)
Internal or private AI models
AI integrations with enterprise systems
Third-party AI services and vendors
Data inputs, outputs, and storage
Without a defined scope, a generative AI security policy becomes difficult to enforce and easy to bypass.
How to Establish an Effective Generative AI Security Policy
Generative AI can dramatically improve productivity, decision-making, and automation but without guardrails, it can also introduce serious security, privacy, and compliance risks. An effective generative AI security policy helps organizations adopt AI safely while maintaining trust, control, and accountability.
1. Define the Purpose and Scope of the Policy
Start by clearly stating why the policy exists and who it applies to.
Key pointers:
Define the business objectives for using generative AI (efficiency, innovation, automation).
Specify which teams, roles, and departments are covered.
Identify which AI tools fall under the policy (public AI tools, enterprise models, internal AI systems).
Clarify acceptable and prohibited use cases.
A clear scope prevents misuse and eliminates ambiguity early.
2. Classify Data and Set Usage Boundaries
Data exposure is the biggest risk in generative AI adoption.
Key pointers:
Define data categories (public, internal, confidential, regulated).
Explicitly prohibit entering sensitive data (PII, financial data, credentials, IP) into public AI tools.
Establish rules for using AI with customer or employee data.
Require anonymization or masking where AI interaction is permitted.
This ensures AI tools don’t become accidental data-leak channels.
3. Establish Access Control and User Permissions
Not everyone needs unrestricted AI access.
Key pointers:
Define who can access which AI tools and models.
Apply role-based access controls (RBAC).
Require authentication and approval for enterprise AI tools.
Restrict model fine-tuning or prompt sharing to authorized users only.
Controlled access reduces insider risk and accidental misuse.
4. Address AI-Specific Security Risks
Generative AI introduces risks that traditional security policies don’t cover.
Key pointers:
Define protections against prompt injection and malicious inputs.
Set rules for validating AI outputs to prevent hallucinations.
Prohibit fully autonomous AI decision-making in high-risk scenarios.
Require human-in-the-loop review for legal, financial, or customer-facing outputs.
This keeps AI as an assistant not an unchecked decision-maker.
5. Ensure Compliance, Ethics, and Responsible Use
AI security isn’t just technical it’s also legal and ethical.
Key pointers:
Align AI usage with data protection laws (GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, etc.).
Define guidelines to prevent biased, discriminatory, or misleading outputs.
Establish accountability for AI-assisted decisions.
Require transparency when AI-generated content is used externally.
Responsible AI usage protects both users and brand reputation.
6. Vet AI Vendors and Third-Party Tools
Third-party AI tools can introduce hidden risks.
Key pointers:
Evaluate vendor security posture and compliance certifications.
Review data retention, training, and ownership policies.
Ensure contractual guarantees on data usage and confidentiality.
Limit shadow AI usage by approving vetted tools only.
Vendor governance prevents supply-chain AI risks.
7. Implement Monitoring, Logging, and Auditing
You can’t secure what you can’t see.
Key pointers:
Log AI tool usage and access activity.
Monitor prompts and outputs for policy violations.
Conduct periodic audits of AI usage patterns.
Review high-risk interactions regularly.
Continuous visibility ensures ongoing compliance and early risk detection.
8. Define Incident Response and Enforcement
AI-related incidents need a clear response plan.
Key pointers:
Define what constitutes an AI security incident.
Establish reporting and escalation procedures.
Assign ownership for investigation and remediation.
Define consequences for policy violations.
Clear enforcement ensures the policy is taken seriously.
9. Train Employees and Review Regularly
A policy only works if people understand it.
Key pointers:
Provide AI security awareness training.
Share real-world examples of AI misuse and risks.
Update the policy as AI capabilities evolve.
Review effectiveness at least annually.
Education turns policy into practice.
Data and Insights: Why Generative AI Security Policies Matter
Studies show that over 60% of employees have used generative AI tools at work without formal approval
Security researchers report that nearly half of AI prompts contain sensitive or proprietary information
Regulatory fines related to data privacy continue to increase globally, making policy-driven AI governance essential
Organizations with a documented generative AI security policy report higher AI adoption confidence and fewer security incidents
These insights reinforce that a generative AI security policy is not a barrier to innovation it is an enabler.
Key Takeaways
A generative AI security policy is essential for safe and scalable AI adoption
Clear scope, data controls, and governance are the foundation of the policy
Data protection is the most critical risk area in generative AI usage
Employee training and enforcement determine real-world effectiveness
Continuous updates keep the generative AI security policy aligned with evolving risks
Read More: How To Develop An AI Ready Network Architecture
Generative AI Security Policy Templates
Here are practical Generative AI Security Policy templates you can adapt for your organization. These are ready-to-use, structured, and cover different scopes—from a short version to a detailed enterprise policy.
1) Short Policy Template (One Page)
1. Purpose: This policy defines secure, compliant use of generative AI tools across the organization.
2. Scope: Applies to all employees, contractors, and third parties using generative AI tools for work.
3. Acceptable Use
• Only use approved AI tools.
• Do not input confidential, regulated, or personally identifiable data into public AI systems.
• Use AI outputs only after human validation.
4. Access Control
• Access is role-based and requires manager approval.
• Enterprise AI tools require multi-factor authentication.
5. Security Requirements
• Follow organizational data classification rules.
• Report anomalies or suspected misuse immediately.
6. Compliance: AI use must comply with data protection and industry regulations.
7. Enforcement: Policy violations may result in disciplinary action.
2) Standard AI Security Policy Template (Department Level)
1. Introduction
This policy governs the secure deployment and use of generative AI within the [Department Name].
2. Definitions
• Generative AI Tools: Systems that produce text, images, code, or other outputs (e.g., LLMs, code generators).
• Sensitive Data: Internal, confidential, and regulated data as defined in the Data Classification Standard.
3. Policy Statements
3.1 Data Protection
• Never submit regulated or sensitive data to public AI models.
• Use approved, secure platforms when processing internal data.
• Anonymize data before AI interaction.
3.2 Access & Authorization
• All AI tool usage must be logged and overseen by IT Security.
• Roles with access: List roles (e.g., Developers, Analysts).
• Privileged usage requires security training completion.
3.3 Security Controls
• Centralized logging of AI interactions.
• Periodic review of prompts, outputs, and access logs.
• Detection & prevention against prompt injection and model misuse.
3.4 Compliance & Audit
• Quarterly audits of AI usage and output quality.
• Alignment with regulatory standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
4. Incident Response
• Define reporting channels (e.g., security@company.com).
• Investigations led by InfoSec within 24 hours of report.
5. Roles & Responsibilities
• Users: Comply and report issues.
• IT Security: Monitor, audit, train, enforce.
• Managers: Approve access, ensure compliance.
6. Review Cycle
Annual policy review or on significant AI ecosystem change.
3) Enterprise-Grade Generative AI Security Policy Template
Use this when your organization has large scale AI deployments, industry regulations, or cross-functional teams.
1. Policy Overview
This policy establishes security, compliance, and ethical standards for generative AI usage across [Organization Name].
2. Applicability
This applies to:
• All employees, contractors, vendors, partners.
• All generative AI systems, integrated tools, internal models, and third-party AI services.
3. Data Classification & Handling
3.1 Data Tiers:
• Public Allowed in AI tools.
• Internal Allowed with masking.
• Confidential & Regulated Prohibited in public IA tools.
3.2 Data Controls:
• Mandatory encryption for all AI data at rest and in transit.
• No storage of sensitive prompts or outputs outside approved systems.
4. Access & Identity
4.1 Role-Based Access Control: Users must be assigned permissions per job function.
4.2 Authentication:
• MFA required for all AI systems.
• Privileged access reviewed quarterly.
5. Secure Usage Guidelines
5.1 Prompt Security:
• Detect and mitigate prompt injection attempts.
• Do not store original prompt text without redaction.
5.2 Output Validation:
• Critical outputs must pass human review.
• Maintain acceptance criteria for model responses.
5.3 Development Practices: Code generated via AI must be scanned and peer reviewed.
6. Monitoring & Logging
• Centralized SIEM logging of AI interactions.
• Alerts for anomalous usage (volume, sensitive keywords).
• Monthly usage reports to risk and compliance teams.
7. Vendor & Third-Party Controls
• Only approved AI vendors with security attestations (SOC 2, ISO 27001).
• Contract clauses ensuring data ownership and usage limitations.
8. Compliance & Legal
• Adhere to privacy laws (GDPR, CCPA, etc.).
• Periodic legal review of AI usage policies.
9. Incident Management
• AI security incidents escalated to InfoSec and Legal within 4 hours.
• Root cause analysis and mitigation within 72 hours.
10. Training & Awareness
• Mandatory AI security training for all employees.
• Specialized sessions for power users and developers.
11. Governance & Review
• AI Governance Committee meets quarterly.
• Policy updates at least annually or upon major AI risk changes.
How to Use These Templates
Customize: Replace placeholders like [Organization Name] and [Department Name] with your specifics.
Align with Standards: Integrate with existing security frameworks (ISO 27001, NIST).
Approve at Leadership Level: Policies should be signed off by CISO/CTO/Legal.
Communicate & Train: Roll out with clear training and FAQs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a generative AI security policy?
Answer: A generative AI security policy is a formal set of rules that governs how generative AI tools are used, what data can be shared, and how risks are managed within an organization.
2. Who should own a generative AI security policy?
Answer: Ownership typically spans security, legal, IT, and business leaders. Clear accountability ensures the generative AI security policy is enforced and updated.
3. Does a generative AI security policy block innovation?
Answer: No, A well-designed generative AI security policy enables innovation by providing safe boundaries and reducing uncertainty around AI usage.
4. How often should a generative AI security policy be updated?
Answer: Most organizations review their generative AI security policy every 6–12 months or whenever major AI or regulatory changes occur.
5. Is a generative AI security policy required for compliance?
Answer: While not always legally mandated, a generative AI security policy significantly reduces compliance risk under data protection and privacy regulations.
